Insider threats in USA are more dangerous as compared to outsider threats, whether via the spread of malware, viruses, or spyware. Companies face great danger from those inside the organization than security threats from outside. However, there are ways to prevent cybersecurity threats from insiders, as discussed in this blog.
Organizations do a pretty good job at protecting against outsider threats and risk agents, but most of us fail at protecting the organization from employees, business partners, contractors, and even customers.
While most of our attention is focused on external threats, insiders cause greater damage as they have better knowledge of our network and business practices inside out. There are plenty of examples out there where employees have caused huge losses to companies. Here are a few to consider:
- A programmer in a North Carolina-based Lance company planted a logic bomb that took sales reps’ computers offline for days. He was simply angered over a demotion.
- Employees of Chase Manhattan Bank stole credit card numbers and used them to seal nearly $100,000.
- An employee in GTE’s Network Service Support Center in Tampa wiped data causing damage of more than $200,000.
Key Cybersecurity Threats From Insiders in USA
It’s not just outsiders that pose a serious threat to organizations. Employees can also sabotage a company’s system through ignorance or a cause. Even a wrong click can lead to massive consequences. So, before moving on towards prevention, let’s take a look at major cybersecurity threats in USA from insiders that you should be looking for.
1. Virus
A virus is a malignant code that can take over any device on an infected system. It can steal passwords, corrupt important files, spam contacts, and more. Viruses are either purposely or accidentally spread.
For example, in January 2019, the city of Akron, Ohio, suffered from a virus attack after two of its employees opened fake invoices through spam emails.
2. Spyware
Any software on a device that is installed without the user’s permission is called spyware. Some common examples of spyware are adware, keystroke loggers, and trojans. Spyware is used for spying on users.
In June 2021, Israeli spyware called Pegasus was found on smartphones worldwide, targeting journalists and activists. It transformed smartphones into surveillance devices without the user knowing about them. To prevent spyware, companies can use antispyware tools like virtual private networks that come with security scan systems.
3. Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software that can steal, encrypt and delete private information. It restricts users from accessing their system unless the ransom is paid. These are distributed via pushing attacks in the form of bogus emails, downloads, or marketing materials. It can also be injected over LAN networks.
Here are a few examples of recent ransomware attacks in the past few months:
- Sinclair TV stations hit by ransomware attack across the US.
- European call center provider, GSS, hit by a ransomware attack on September 18, 2021.
- A $5.9 million ransomware attack on a US farmer cooperative, NEW Cooperative Inc., took down the whole system.
How to Prevent Insider Cybersecurity Threats in USA 2023
With so many high-profile cases of insider threats and cybersecurity incidents, what can organizations do about it? Here are ten tips to help you implement insider threat mitigation at your organization and prevent possible incidents from happening in USA.
1. A detailed security policy
Make sure you have a detailed security policy in place that includes what is expected of employees and procedures to prevent misuse and consequences in case someone is found breaching the law.
Start by analyzing your current security policies and identify gaps. Make sure your policy details the limits of information access to a few employees. Specify who is allowed to access the data and under which circumstances the information can be shared.
2. Physical security is important
When it comes to cybersecurity, people completely neglect physical security. Consider physical security your #1 priority, you can check security people from Craigslist. You can prevent insider threats and incidents to a great extent by keeping people away from your critical infrastructure and isolating critical systems in restricted areas.
Red Dot, a Seattle heating and cooling company, faced losses of thousands of dollars as two janitors combed through garbage cans and cabinets, stealing employee personal information. They stole tens of thousands of dollars by obtaining credit cards.
3. Strong Authentication
It is the 21st century, and password hacking technology has evolved quite a lot. There are algorithms that run for days, trying every possible combination to hack into accounts. Then there are employees using post-its on monitors with passwords on them, and not to mention multiple employees sharing a password.
A cost-effective way to protect passwords is by using multi-factor authentication for sensitive applications and systems. You can even combine passwords with user IDs, fingerprint readers, or smart cards for more security. This can also protect you against potential data breaches.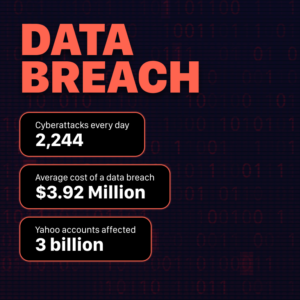
4. Segment networks
Network-based intrusions should be at the top of your internal cybersecurity defenses. If your organization has one un-segmented LAN network, a single attack can render it insecure.
The best way to secure your network is to have different segments of LAN with firewalls. It will also make it easier for your IT team to identify choke points and possible compromised locations.
5. Prevent information leaks
Sensitive data and information can flow out of your organization through emails, messaging, and more. Combine security and security policies to prevent information leaks. First, make sure your employees understand the restriction on the dissemination of confidential data.
Make sure you have an intrusion detection system (IDS) in place so it can scan your business communication systems for unique phrases. It will give alerts when it sees certain snippets on the network. Email firewalls can also check all outgoing emails to prevent accidental information leaks.
6. Secure hardware
You cannot be dependent on your employees for taking the responsibility of device security. Group your privacy policies and allow IT security managers to configure the operating systems, including apps.
If you’re using Microsoft’s Active Directory service, then you should be able to lock down desktops across the organization in case of emergencies. In addition, make sure every desktop at the company has all the required tools like a VPN, NET firewalls, and anti-malware installed and running.

7. Investigate all unusual activities
Unlike outside attackers, insiders are not careful about converting their tracks because they are not expecting to be caught in the first place. According to Peter Vestergaard, a former technical manager at Danish security consultancy Protego said:
“Generally none of the insider attacks we have seen were difficult to investigate. The biggest problem has been that companies don’t have sufficient logging. In one case, almost no one knew that logging on a non-domain controller NT/Win2K server is disabled by default. Therefore, little or no log material was available.”
To make sure nothing goes unnoticed, it’s best to have network forensic analysis tools so you can analyze the flow of information on your network.
8. Screen new employees
If you want to prevent insider threats in USA, spend more time investigating employee backgrounds before hiring them. If you cannot do background checks, consider outsourcing instead.
The screening takes a lot of time as you cannot know much about the employee by just looking at his current address. You can make calls to their previous employers to check why they are switching the job.
9. Implement Strategies
Just like you implement strategies for servers on public Wi-Fi, make sure you do the same on your internal servers. Try locking down configurations to limit access and increase security protocols.
Get rid of all unused accounts and emails. Make sure everything is patched. Close down accounts of your ex-employees to decrease vulnerabilities in the system.
10. Monitor employees for misuse
Last, but not least, monitor your employees directly. It can be done through security cameras or keystroke logging. Your employees will be against it, but you can never be too sure about the protection of your company’s private data and information. However, make sure you stay in the loop of legal monitoring in your jurisdiction.
By having a security policy in place along with insider threat detection techniques, you can protect your company’s sensitive information. Make sure your employees are well aware of the legal consequences they will have to face if found in violation of the security policy. Your employees could be violating your trust, stealing sensitive information that could cost you thousands of dollars.
Wrapping Up!
Cybersecurity damages to the global economy are expected to reach $6 trillion by the end of 2021. This year, we saw a rapid increase in cyberattacks across different industries, and the trend doesn’t seem to be dying down anytime soon. These are ten tips on preventing cybersecurity insider threats in USA that can be implemented today.
Before jumping on the bandwagon, make sure you understand your organization’s security needs and loopholes. There are plenty of things that can be done to secure sensitive company information without violating your employee’s privacy, as discussed above.
Most of the techniques mentioned above can do more than just boost security; but can also make sure you don’t have to face public humiliation in the wake of a data breach.

